Sodium batteries are batteries that use sodium ions as charge carriers. Batteries charge and discharge by inserting and separating sodium ions between positive and negative electrodes. Sodium batteries work on basically the same principle as lithium batteries, except for a different charge carrier.
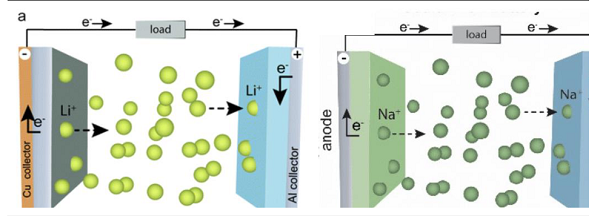
Both sodium and lithium batteries are rechargeable batteries, but there are some differences and advantages between them:
The chemical composition is different: the positive electrode material used in the sodium battery is a sodium compound, while the lithium battery uses a lithium compound as the positive electrode material. Sodium, by contrast, is more readily available and cheap, while lithium is scarce and expensive.
Energy density difference: Sodium batteries have about half the energy density of lithium batteries, which means they are typically larger and heavier than lithium batteries of the same capacity. However, the energy density of sodium batteries is gradually increasing, and may be equal to or even exceed that of lithium batteries in the future.
Environmental protection: Sodium batteries use more abundant resources, so they have more advantages than lithium batteries in terms of environmental protection. At the same time, since most of the chemical components used in sodium batteries are non-toxic and renewable, the waste generated is less polluting to the environment.
Safety: The electrolyte of sodium batteries is highly flammable and corrosive, so there are high safety requirements in design and manufacture. Lithium batteries are relatively stable, but there are also safety hazards such as overheating, short circuit, and explosion.
Different application scenarios: Due to the low energy density, sodium batteries are usually used in occasions that do not require high weight and volume, such as energy storage systems, industrial vehicles, etc. efficiency and high-performance applications such as mobile devices and electric vehicles.
To sum up, sodium batteries and lithium batteries have their own advantages and disadvantages. Which one is better depends on the application scenarios and actual needs. In the future, as sodium battery technology continues to develop, it may become a more competitive renewable energy solution.



